Android security is always a hot topic on these here Nets of Inter — and almost always for the wrong reason.
As we’ve discussed ad nauseam over the years, most of the missives you read about this-or-that super-scary malware/virus/brain-eating-boogey-monster are overly sensationalized accounts tied to theoretical threats with practically zero chance of actually affecting you in the real world. If you look closely, in fact, you’ll start to notice that the vast majority of those stories stem from companies that — gasp! — make their money selling malware protection programs for Android phones. (Pure coincidence, of course.)
The reality is that Google has some pretty advanced methods of protection in place for Android, and as long as you take advantage of those and maintain a teensy shred of common sense, you’ll almost certainly be fine (yes, even when the Play Store guards slip up and let the occasional bad app into the gates). The biggest threat you should be thinking about is your own security surrounding your devices and accounts — and all it takes is about 20 minutes a year to make sure your setup is sound.
Take the time now to go through this checkup, then rest easy over the next 12 months with the knowledge that you’re in good shape — and that the mean ol’ Android malware monster won’t be bangin’ down your virtual door anytime soon.
[Psst: Want even more advanced Android knowledge? Check out my free Android Shortcut Supercourse to learn tons of time-saving tricks for your phone.]
Part I: App and web intelligence
Android security step #1: Look over all the apps and services connected to your account
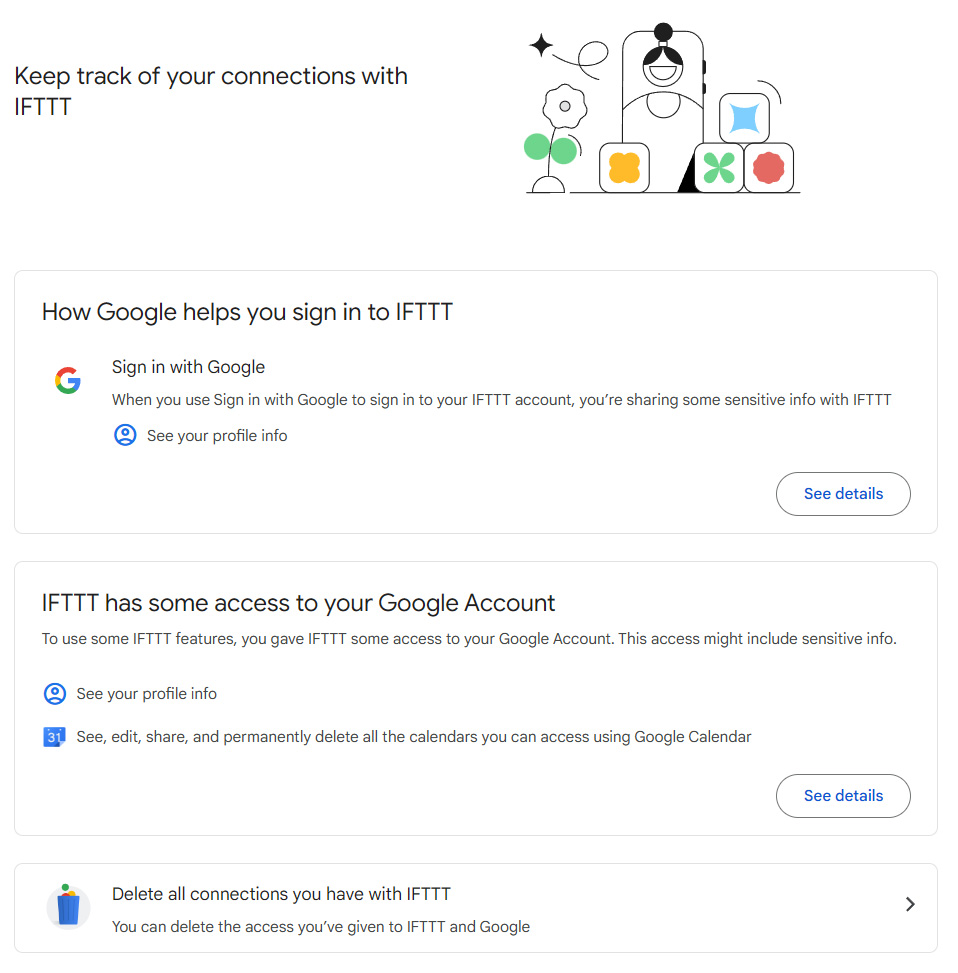
You’ve probably granted countless apps access to parts of your Google account over time — which is no big deal in general, but with any apps you’re no longer using, it’s a smart idea to close the connections.
Visit this page in Google’s security settings to see a list of everything that’s authorized and what exactly it can access. If you encounter anything you don’t recognize or that you no longer use, click it and then click the “Delete all connections” option to give it the boot.
JR Raphael, IDG
While you’re at it, take two minutes to look through the list of apps on your phone and uninstall anything you’re no longer actively using. That’ll eliminate unnecessary windows to different areas of your data — and as an added bonus, it’ll free up space and cut down on potentially phone-slowing resource use, too.
Android security step #2: Revisit your Android app permissions
Speaking of dusty old skeletons on your device, it’s all too easy to grant an app access to some sort of information without giving it much thought during that initial setup process. That’s why it’s well worth checking in periodically to remind yourself what permissions the apps on your phone possess — and to see if any of ’em go beyond what seems reasonable or necessary.
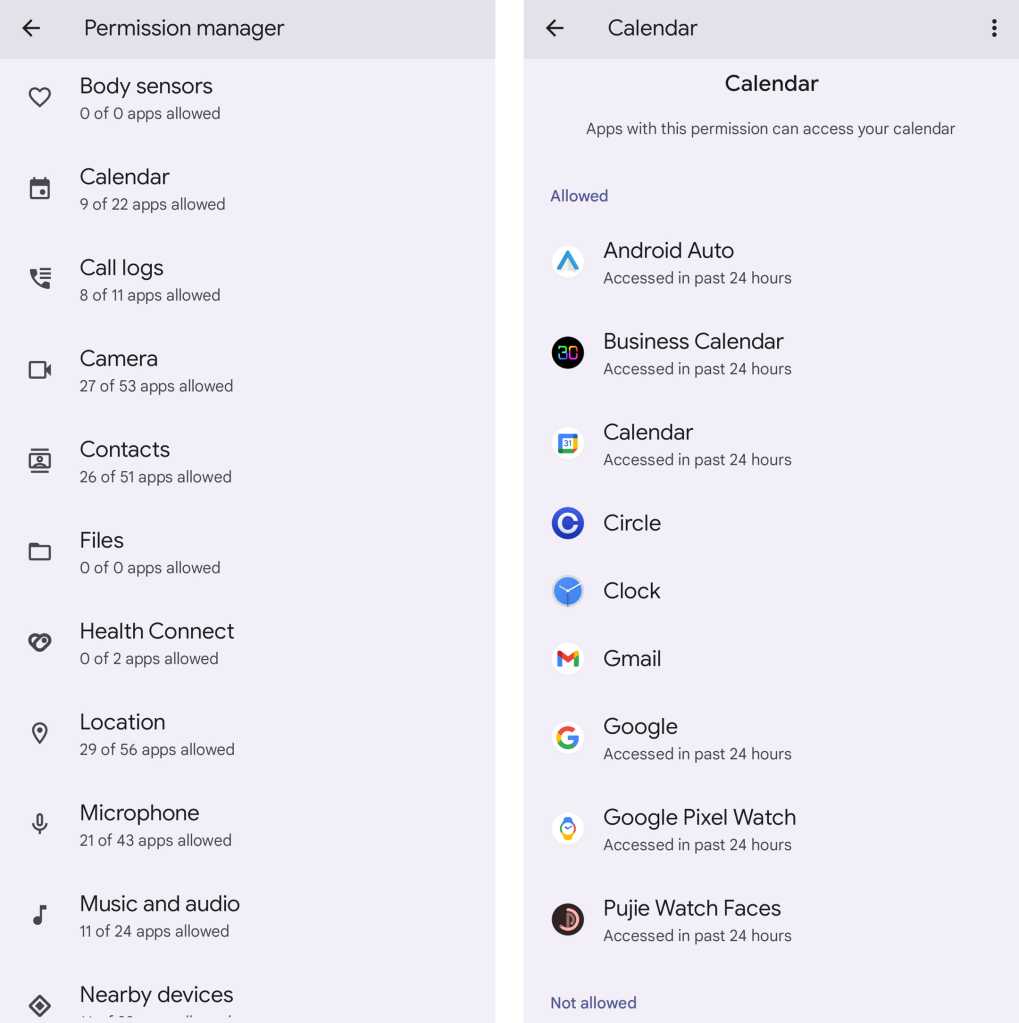
With recent Android versions, you can just open up the Security & Privacy section of your system settings and look for a line that says “Permission manager.” Depending on your specific software and device, you might have to first tap a line that says “Privacy” before you see it. (If you don’t see anything like that, try searching your system settings for the word permissions to find the closest equivalent.)
Whatever it’s called and however you get there, you should ultimately end up facing a collection of categories for all the types of permissions you’ve granted to apps on your device over time. Take a peek through ’em all and see what you find. If you see anything that raises an eyebrow, all you’ve gotta do is tap it to revoke the access.
JR Raphael, IDG
For even more insight, look for the “Privacy dashboard” option within that same section of your system settings (or “Permissions used in last 24 hours,” in Samsung’s vernacular). That’ll let you see exactly which apps have actually accessed different permission-requiring areas over the past 24 hours.
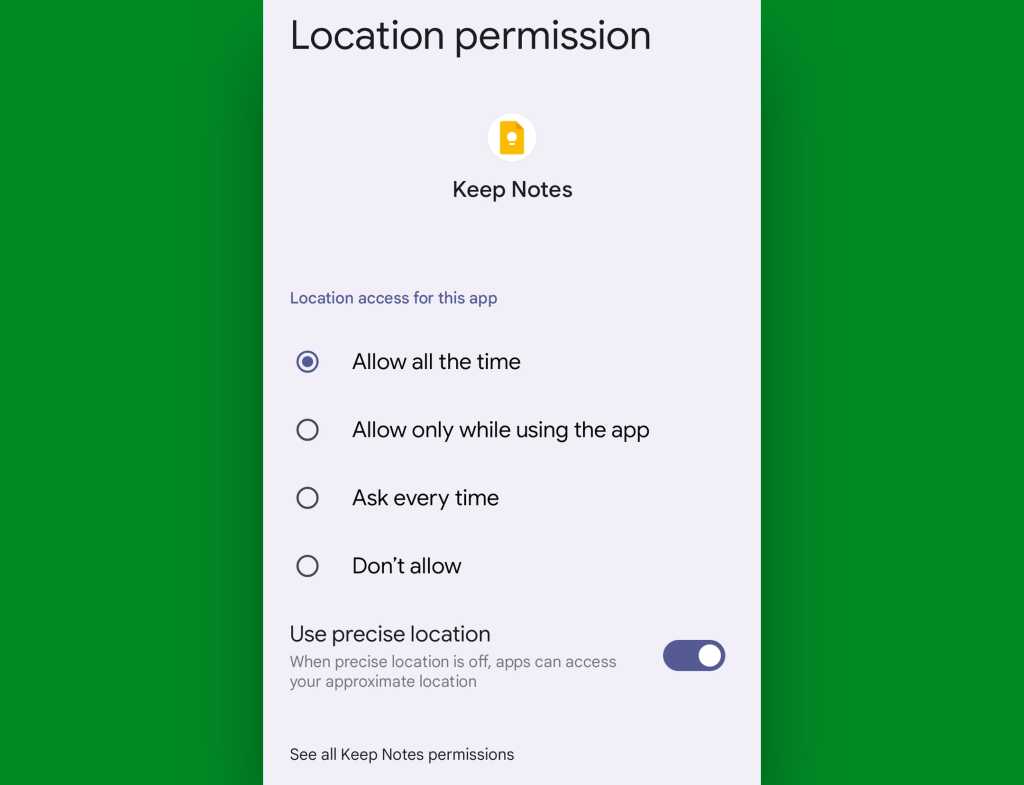
And remember, too: With Android 10 and higher, you can go a step further when it comes to location and allow an app to access that only when you’re actively using it. With Android 11 and up, you can get even more nuanced and grant apps only temporary, case-by-case permissions to access your location, camera, and microphone. And as of Android 12, you can fine-tune an app’s location access to make it only approximate instead of precise, if you like.
You’ll find all those options within any relevant app’s settings, once you dig into one of those related permissions:
JR Raphael, IDG
Critically, in all of those cases, it’s up to you to go through your settings and make the associated changes — especially when it comes to apps you had on your device before the relevant Android upgrade reached you and the latest options for permission control became available.
Android security step #3: Verify that you’re using Android’s app-scanning system
Android has long had the ability to monitor your device for harmful code or suspicious activity — no third-party apps or add-ons required. And while the system is now automatically enabled on any reasonably recent device, it’s a good idea to occasionally confirm that everything’s turned on and working the way it should, if for no other reason than to remind yourself that such a system is present and working on your behalf.
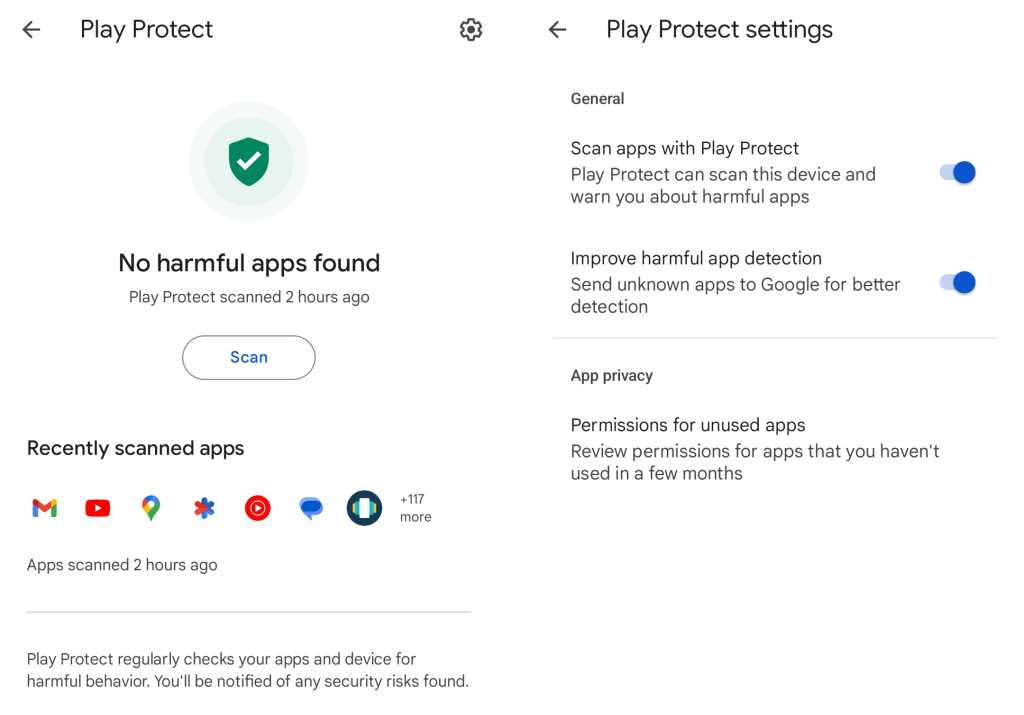
So mosey back over to the Security & Privacy section of your system settings, tap the line labeled “App security,” then tap “Google Play Protect” and take a peek at the system’s latest activity. You can also tap the gear icon in the upper-right corner of the screen to confirm that all available toggles are on and active.
JR Raphael, IDG
That’ll allow Android’s app verification system to keep an eye on all apps on your device, even after they’re installed, and make sure they don’t do anything dangerous. The scanning will run silently in the background and won’t ever bother you unless something suspicious is found.
Odds are, you’ll never even know it’s there. But it’s a valuable piece of protection and peace of mind to have, and it’s a good idea to keep it in the back of your mind that it’s present.
Android security step #4: Fight phishing
Even the savviest tech user can fall prey to a well-hatched phishing scheme — an effort by some ne’er-do-well to trick you into willingly giving up sensitive info, usually by making an email, text, or other digital request look like it’s from some official source that needs to confirm an account number or something else along those lines.
Suffice it to say, any extra layer of protection from such tactics can only be a good thing. And if you’ve got a Google Pixel phone, good news: There’s a relatively new option available to you that watches out for any known deceptive patterns and warns you about ’em before they’re able to manage any damage.
On any current Pixel device, head into the Security & Privacy section of your system settings, tap “More security & privacy,” then scroll down and tap “Scanning for deceptive apps.”
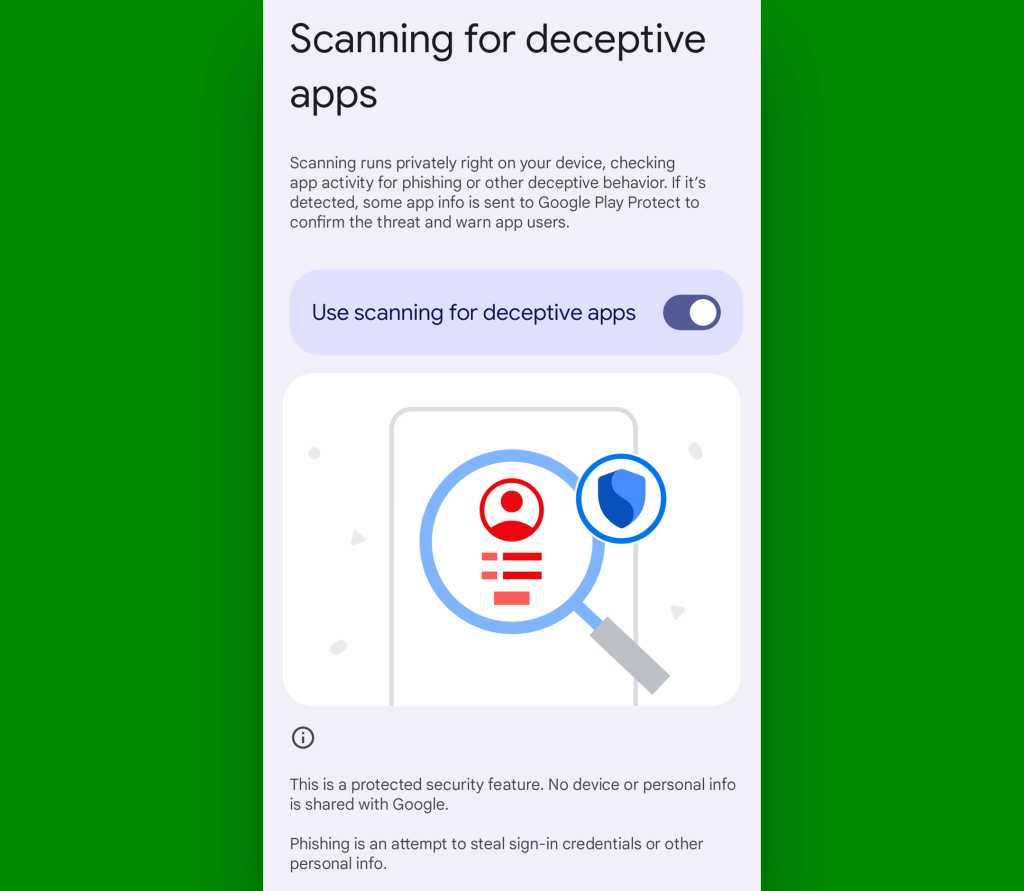
JR Raphael, IDG
Make sure the toggle on the screen that comes up next is in the on and active position, then breathe easy with the assurance that Google’s got your back when it comes to any phishing attempts cast in your direction.
Android security step #5: Weave a stronger web safety net
Along with phishing, one of the most likely threats to your Android security is your own lapse in judgment whilst wading around these ever-murky web waters of ours. (Sensing a theme here yet?)
Provided you’re using Google’s Chrome Android browser, though, there’s an easy way to create an extra layer protection in that arena as well.
Just tap the three-dot menu icon in Chrome’s upper-right corner, then select “Settings” followed by “Privacy and security” and “Safe Browsing.” Now, consider which level of protection seems most sensible for you:
- Standard protection, which warns you if you try to open a site or download a file that’s known to be dangerous.
- Enhanced protection, which goes a step further and protects your Android web browsing in real-time — by instantly scanning every page you open and file you download and then warning you of anything potentially concerning, even if it isn’t already a known threat. (This path does require limited data about your browsing activity to be sent to Google’s servers for analysis, but Google has clear promises in place about exactly how that data is protected and secured from any manner of unexpected use.)
Pick the path you feel most comfortable pursuing, and know that your web adventures now have that extra safety net around ’em.
Android security step #6: Appraise your app-downloading IQ
If you’re reading this column, I probably don’t need to tell you this — but I will, anyway: While we’re thinking about the subject of Android security, take on a teensy bit of responsibility and commit to letting common sense guide your app-downloading decisions.
Let’s not kid ourselves: Google’s security mechanisms are invariably gonna fail on occasion. There’s no getting around that. But even when a shady app makes its way into the Play Store, all it typically takes is the tiniest shred of awareness to avoid having it affect you.
Just as you do when browsing the web from a computer, look at something before you download it. Look at the number of downloads and the overall reviews. Think about what permissions the app wants and whether you’re comfortable with the level of access it requires. Click the name of the developer, if you still aren’t sure, and see what else they’ve created. And unless you really know what you’re doing, don’t download apps from random websites or other unestablished third-party sources. Such apps will still be scanned by Google’s on-device security system before they’re installed, but your odds of encountering something shady are significantly greater out in the wild than within the Play Store.
(Your Android device won’t let you download apps from unknown sources by default, by the way, so if you ever try — even inadvertently — you’ll be warned and prompted to authorize that specific form of non-Play-Store download. Apps on Android will never magically install themselves without your explicit authorization, nor will they ever be able to access any sensitive sensors or areas of data unless you grant ’em the associated permission.)
By and large, all it takes is a 10-second glance to size something up and see if it’s worth installing. With all due respect to the dodos of the world, it doesn’t take a rocket scientist to stick with reputable-looking software and avoid questionable creations.
Part II: Passwords and authentication
Android security step #7: Double-check your digital sentinels
A quick no-brainer that’s important to mention: If you aren’t using biometric security and/or a PIN, pattern, or password on any of your devices, start doing it. Now.
Talk to any security expert, and you’ll hear the same thing: The most likely cause of a security failure is simply a failure on your behalf to secure your stuff. You are the weakest link, as the cool kids said 20 to 47 years ago.
Embarrassingly dated pop culture references aside, think about it: If your phone has no passcode protecting it, all of your data is just out there and waiting for the taking anytime you leave the device unattended (intentionally or otherwise). That includes your work and personal email, work and personal documents, work and personal social media accounts, and any and all photos associated your phone (yes, even those photos — hey, I’m not here to judge).
The best part: Android makes it hassle-free as can be to keep your devices secure. The software’s Smart Lock function (which is curiously in the midst of being rebranded to Extend Unlock, for reasons I can’t even begin to fathom) allows you to automatically leave your phone unlocked in a variety of preapproved “safe” conditions — like when you’re at home or the office, when a specific trusted Bluetooth device is connected, or even when the phone is being carried in your pocket. That means the extra security shows up only when it’s really needed, and you don’t have to mess with it the rest of the time.
You can typically find and set up Smart Lock/Extend Unlock in the Security section of your system settings, typically tucked away behind an “More security & privacy” option — or, on Samsung devices, within the Lock Screen section of the system settings. If all else fails, just search your system settings for Smart Lock or Extend Unlock to turn up the available options.
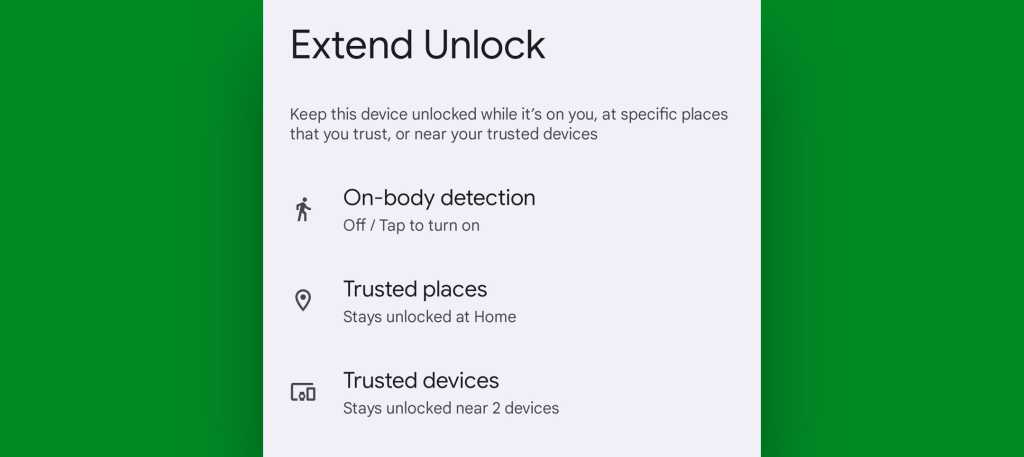
JR Raphael, IDG
Plain and simple, there’s no excuse to leave your stuff unprotected. Head into your device’s settings to get started this second, if you haven’t already.
Android security step #8: Peek in on your saved passwords
One of the less frequently discussed parts of Google’s security system is its ability to save passwords for websites and apps accessed via your mobile devices, as part of what’s now known as Google Password Manager. So as part of your annual checkup, glance over the list of saved passwords Google has for your account to remind yourself what’s there and see what, if any, of your credentials have been compromised (which Google will plainly warn you about at the top of that very same screen).
While you’re at it, take a few seconds to remove any dated items that are no longer needed and don’t belong. Your future self will thank you.
Android security step #9: Assess your password management system
Google’s password manager is better than nothing, but you’ll get stronger security assurances, more advanced and useful features, and broader support for in-app password filling by using a dedicated password management service.
We’ve got some commendable Android password manager choices, too, with my own current recommendations revolving around 1Password for most people and Bitwarden for anyone who needs a free path or prefers a self-hosted setup. Both services work equally well on the desktop front and even on iOS, with the main differences revolving around cost, extra features, interfaces, and the resulting overall user experiences.
If you aren’t using one of those services, now’s the time to start. And if you are already using such a service, take a few minutes now to peek into the app’s settings and make sure you’re taking advantage of all the on-device protection it offers. With 1Password, for example, you should confirm that the app is set to be protected by either biometric security or a password and that it’s configured to automatically lock within a few minutes after you stop using it. The app can also automatically clear your system clipboard of any passwords you copy after 90 seconds, which is a smart pinch of added protection to have. (All of those options are in the Security section of 1Password’s settings.)
Like Google, most good password managers also now provide an option to analyze all of your passwords and identify any that would be advisable to change — ones that are duplicated or otherwise not as strong as they could be. That’s another smart thing to check up on as part of this annual audit.
Android security step #10: Evaluate your two-factor authentication situation
A single password isn’t enough to protect an important account these days — especially one as wide-reaching and valuable as your Google account. Two-factor authentication makes it so that you have to either confirm the sign-in on an approved physical device or put in a special time-sensitive code in addition to your password anytime you try to sign in. That significantly increases your level of security and decreases the odds of anyone ever being able to break in and access your personal data, since they’d need both knowledge of your password and the physical presence of your key-like device to do it.
If you don’t yet have two-factor authentication enabled for your Google account, head over to this site to get started. And don’t stop with just Google, either: Look into enabling two-factor authentication on any service that offers it, including your password manager, your social media accounts, and any non-Google cloud storage services that you use.
If you really want to keep your account secure, Google also offers a souped-up option called Advanced Protection. It requires you to purchase physical security keys and then use those anytime you sign into your Google account. It also severely limits the ways in which third-party apps can connect to your account. That sort of elevated and locked-down setup probably won’t be sensible for most folks, but if you feel like you need the extra protection, you can learn more and enroll here.
Android security step #11: Optimize your lock screen security
Your lock screen is the guard of your Android device’s gate — and there are a few things you can do to beef up its muscle and make sure it’s fully prepared for the job.
First, think about the types of notifications you get and how much of that info you want to be visible on your lock screen — since anyone who gets their hands on your phone could easily see all that data. If you tend to get sensitive messages or just want to step up your security and privacy game a notch, head into the Display section of your system settings and select “Lock screen” — or, if you’re using a Samsung phone, look in the separate Lock Screen section of your system settings instead.
There, you’ll find tools for controlling precisely what will and won’t be shown in that pre-authentication area as well as for creating a security-minded message that’ll always appear on your lock screen — for instance, something like: “If found, please call Joe T. Schmo at 333-222-1111.” You could even consider adding an emergency contact into your settings and then using the lock screen message to direct people to that information.
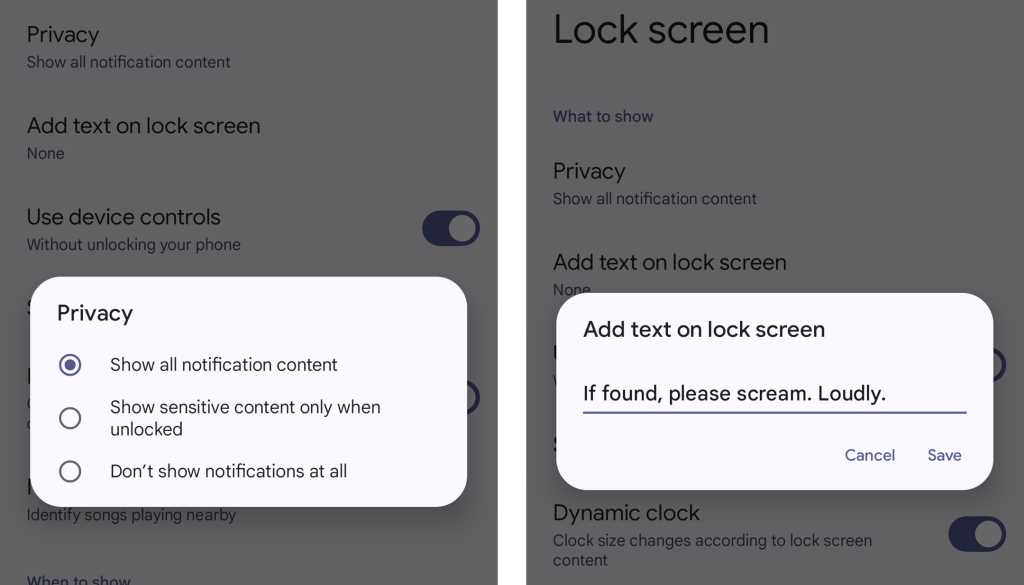
JR Raphael, IDG
And finally, provided your phone is running Android 9 or higher, an option called lockdown mode is well worth your while to activate or just remind yourself about. Lockdown mode gives you a fast way to lock your phone down from all biometric and Smart Lock/Extend Unlock security options — meaning only a pattern, PIN, or password could get a person past your lock screen and into your device.
The idea is that if you were ever in a situation where you thought you might be forced to unlock your phone with your fingerprint or face — be it by some sort of law enforcement agent or just by a regular ol’ hooligan — you could activate the lockdown mode and know your data couldn’t be accessed without your explicit permission. Even notifications won’t show up on your lock screen when that mode is activated, and that heightened level of protection will remain in place until you manually unlock your phone (even if the device is restarted).
There’s just one catch: On some devices — including Samsung phones — it’s up to you to enable the option ahead of time in order for it to be available. But doing so takes only a couple of seconds: Search your system settings for lockdown and then look for the toggle to enable it. (If you don’t see any such option at all, odds are, you’re using a Google Pixel phone and/or a recent enough Android version that it’s just on and enabled by default.)
Then, if the need ever arises, remember this: In your phone’s power menu, along with the regular options for restarting and shutting down your device, you’ll always find a button to activate that “Lockdown” function. Hopefully, you’ll never need it — but now you’re ready in case you do.
And with that, guess what? You’re more than halfway done with this annual checkup. Not too painful so far, right? Only seven more steps to go…
Part III: Device access
Android security step #12: Clean up your list of connected devices
Anytime you sign into a new device with your Google account — be it an Android phone, a Chromebook, or even just the Chrome browser on a regular PC — that device is added to an approved-for-access list and associated with your account.
Click over to this page in Google’s security settings and give your list a once-over. If you see any old devices you no longer use, click on ’em and then click the “Sign Out” button that pops up to make sure they no longer have access to your account. And if you see any devices you’ve never used, remove ’em right away — and then go change your Google account password immediately.
Android security step #13: Clean up your devices in the Play Store
This one isn’t directly related to security, but it’s a good bit of housekeeping to perform while you’ve got your cleaning hat on: Head over to the Google Play Store Devices tab and look at your list of available devices. These are the devices that show up as options every time you install a new app from the Play Store web interface — and also the devices that show up as options in Google’s Find My Device utility (more on that in a sec).
Go ahead and uncheck the box next to “Show in menus” for any devices you no longer use. And if you see any devices with cryptic codenames, click the “Edit” button alongside ’em and rename ’em to something you’ll recognize.
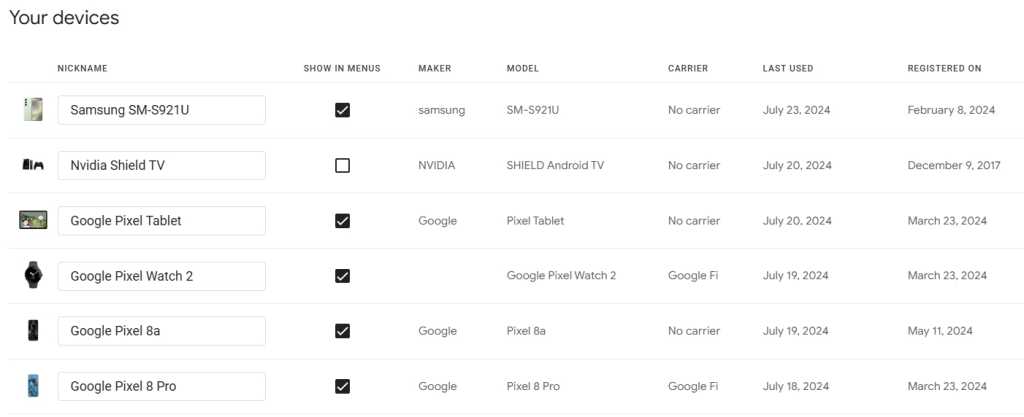
JR Raphael, IDG
The next time you download an app or remotely locate one of your devices will be a much smoother experience as a result.
Android security step #14: Make sure your device is prepared for the worst
Speaking of remote location, you might not realize it, but Google has its own utility for tracking, finding, and remotely wiping an Android device in case you ever lose it — and the whole system is built right into the operating system.
So what are you waiting for? Make sure all of your phones, tablets, and other associated devices are enrolled now, before it’s too late. Just follow my quick ‘n’ simple Find My Device setup instructions for any device you’ve got on or around ye.
Now bookmark the web version of Find My Device and/or download the app on a Chromebook or any other Android-compatible device you own. If you ever can’t find any of your devices, open the service — and you’ll be able to pinpoint precisely where the missing gadget was last seen. You can also force most phones or tablets to ring as well as remotely lock or erase ’em entirely.
Android security step #15: Think about whether you should be using a VPN
No matter how secure your Android phone itself is, someone could theoretically still snoop on your sensitive info if you’re transmitting it over an insecure network. That’s where virtual private networks, or VPNs, come into play: They encrypt all of your incoming and outgoing data so that no one could intercept it and see what you’re doing at the network level.
VPNs aren’t something everyone needs to worry about, but if you use your phone for a fair amount of business work or with any other type of sensitive material, it’s something you ought to at the very least consider — particularly if you use a lot of open Wi-Fi networks, where snooping can be a genuine concern (at least, in scenarios where a site or service’s traffic isn’t already encrypted).
So where to start? Well, first, some companies provide their own custom VPN services for employees. If that’s the case for you, congratulations! You’re already all set.
If you’re using the Google Fi wireless service, the answer is similarly simple: Fi now provides an option to automatically encrypt all of your network connections via Google’s VPN service. All you’ve gotta do is activate it.
The same goes for Pixel phones, which come with Google’s own VPN service as a free and readily available option.
Otherwise, you’ll have to turn to a third-party Android VPN service in order to gain that added level of protection.
Part IV: Big-picture thinking
Android security step #16: Make sure you’ve done your virtual estate planning
We’ve got one more bit of “what if” preparation to address — and it’s slightly unpleasant to think about: If something bad were ever to happen to you, would you want someone else to be able to access your Google account and all the data associated with your devices? With a company-controlled account, it’s less of a worry. But if you’re using a personal Google account and/or maintaining your own Workspace setup for a small business, you don’t want to let that go unaddressed. Take a moment to prepare for the possibility now, and it’ll make things infinitely easier for your friends or loved ones in the event that you ever develop a mild case of, erm, death.
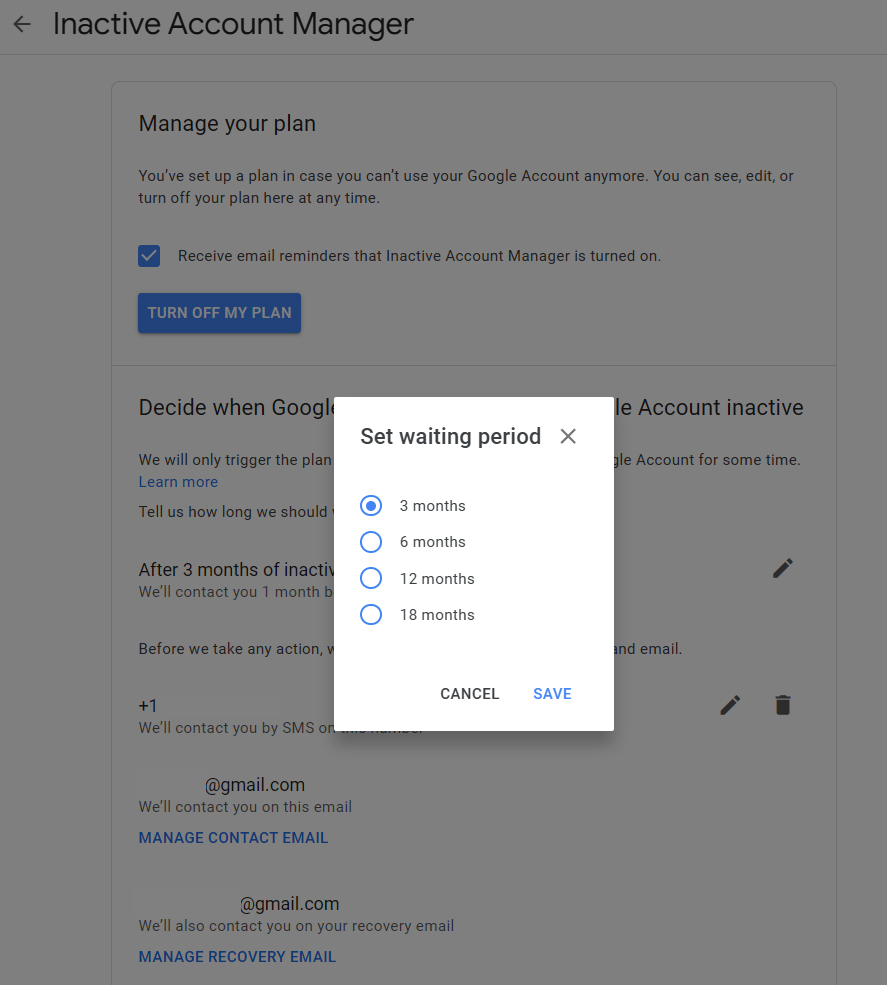
It’s actually pretty painless to do (the preparation, that is — not the death): Just go to this page and make sure you’ve set up Google’s Inactive Account Manager. That system detects when your account has been inactive for a certain period of time — three months, six months, a year, or a year and a half, depending on your preference — and then notifies a trusted contact of your choosing and provides them with whatever level of access you want. You can even set up an auto-reply to kick in for your Gmail (creepy!), and you can tell Google to delete a personal account altogether after a specific amount of time has passed.
Inactive Account Manager is designed to be extraordinarily cautious, with numerous fail-safes in place — including an option to try to contact you via SMS and email a month before your inactivity plan goes into action.
JR Raphael, IDG
Some other services, including 1Password, offer similar systems for setting up emergency access to your account in an extreme situation. There’s also a clever free (and open source!) service called WeExpire that lets you create secure dockets of info that can be shared via QR code in a similar sort of way.
It’s a strange part of security to consider, but — just like with every other area we’ve discussed so far — it’s something worth thinking about and preparing for before the need arises.
Android security step #17: Perform a general Google security check to round things out
Take a deep breath: We’re almost done! This next-to-last step will take you through a broad security check that’ll look for any remaining weak points in your Google account and Android security and then prompt you to fix ’em right then and there.
Just go to this Google security site and click through any issues it presents. It’ll confirm that you’ve successfully performed some of the actions we’ve already discussed and then look for any other potential red flags or opportunities for improvement.
Consider it your confirmation that your personal security setup is A-OK.
Android security step #18: Think carefully about third-party security suites
Last but not least: Now that you’ve made sure your Android security situation is shipshape, think about any third-party security suites you’re using (whether you installed ’em yourself or they came preinstalled on your phone or tablet) and what they’re actually adding to your device.
You’ve already verified that your device is protected. Android is actively scanning for threats on several levels, both on the server side at the Play Store and on your phone as new apps arrive (from any source) and continuing over time. Plus, you’re exercising basic smarts about what apps you download. The operating system could even be looking out for phishing scams, and the Chrome Android browser is keeping an eye out for web-based threats as well.
Beyond all of that, your devices are all enrolled in a sophisticated cross-platform system for remotely tracking, pinging, and erasing as needed. And all of that is happening on the native platform level.
So given those layers, is the third-party security suite on your phone doing anything that isn’t redundant and unnecessary? It’s probably eating up system resources and impacting performance for no real reason — and quite likely also costing you money you don’t need to be spending — but is it actually accomplishing anything of value that Android itself isn’t already handling in a more direct manner?
Unless you’re relying on the app for supplementary services like added anti-theft detection and payment protection, the answer is almost certainly no. If having an extra security layer makes you feel safer, hey, do what works for you. But if you’ve completed every step of this checkup, there’s really no reason you need it — and every reason to send it packing. (To be clear, there are plenty of privacy and security apps that could be worth your while; they just aren’t the silly, bloated device-scanning suites that are so popular among folks who don’t know better.)
And with that, my fellow Android-adoring security-seeker, your checkup is complete. All that’s left is to set yourself a reminder to revisit these same steps this time next year. The areas we’ve just covered are constantly evolving, and giving yourself an annual once-over is the best way to ensure you’re always in tip-top shape.
Get six full days of advanced Android knowledge with my free Android Shortcut Supercourse. You’ll learn tons of time-saving tricks for your phone!

